Abstract
Introduction
Monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL), monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), and clonal hematopoiesis (CH) are three common premalignant hematological conditions. MBL is a precursor to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), MGUS is a precursor to both multiple myeloma (MM) and Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM), and CH is a possible precursor to myeloid disease. All three conditions are independently associated with aging. Furthermore, there is evidence that all three conditions are associated with increased risk of infection. The relationship among these conditions, the prevalence with which they co-exist, and the association between the number of premalignant conditions and risk of infection is unknown.
Methods
Study participants from the Mayo Clinic Biobank, a large-scale biorepository of adult patients, provided a peripheral blood sample between 7/14/2009 to 06/18/2015. Individuals were screened for MBL using eight-color flow cytometry capable of detecting clonal B-cells to the 0.005% level. MGUS was screened using a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF) assay. CH was screened using a targeted sequencing panel of 42 CH-associated genes with at least 1000x read depth and the ability to detect variant allele fractions down to 1%. All study participants resided in Olmsted County, Minnesota, the county that includes Mayo Clinic. Serious infection, defined as hospitalization due to infection, was abstracted from medical records from the time of sample collection through 12/31/2020 or date of death. The medical record abstractor collecting data was blinded to condition. Logistic regression was used to estimate odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the association between each of the conditions. Cox regression was used to estimate hazard ratios (HR) and 95% CI to assess the association between number of premalignant conditions with risk of infection. All analyses were adjusted for age at sample collection and sex.
Results
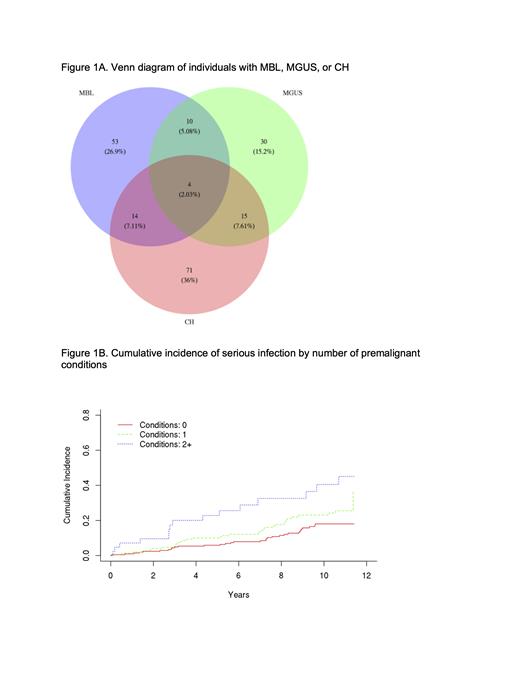
A total of 407 individuals (55% male, median age 68 years) were screened for all three conditions. The prevalence was 19.9% (n=81) for MBL, 14.5% (n=59) for MGUS, and 25.6% (n=104) for CH. When we evaluated the association between each of the conditions, we found no evidence of an association between the prevalence of CH and risk of MBL (OR=0.79, 95% CI: 0.43-1.42), CH and risk of MGUS (OR=1.24, 95% CI: 0.66-2.27), or MGUS and risk of MBL (OR=1.32, 95% CI:0.66-2.52). The prevalence of co-existence of these conditions was assessed by grouping individuals based on their condition or conditions (Figure 1A). We found that 197 (48.4%) study participants had at least one premalignant condition and 10.6% had two or more. Individuals with 2 or more conditions were the oldest (median age 74 years), followed by 1 condition (median 69 years) and 0 conditions (median 67 years, P-trend <0.001). Sex was not significantly different across the groups, with 55%, 58%, and 47% male for 0, 1, and 2 conditions, respectively. Medical record abstraction identified 97 serious infection events in 80 individuals. Medical records were not available on 7 individuals. The most common infections were urinary tract (20 events), pneumonia (14 events), and cellulitis (14 events). Median follow-up time was 10.6 years (range 0.1-11.5 years). Compared to individuals with no condition, MBL (HR=1.75, 95% CI: 1.06-2.88) and MGUS (HR=1.75, 95% CI: 1.04-2.93) were associated with increased risk of serious infection. We found no evidence of an association with CH (HR=1.15, 95% CI: 0.71-1.87). When grouped by the number of conditions, we observed a significant trend (P-trend <0.01, Figure 1B) in risk of serious infections by the number of conditions: individuals with 1 condition had a 35% increased risk of infections (HR=1.35, 95% CI:0.83-2.20) and individuals with 2 or more conditions had a 2.6-fold increased risk (HR=2.58, 95% CI: 1.37-4.84).
Discussion
At least one premalignant condition was present in nearly 50% of the study population, with CH being the most prevalent. No evidence of a relationship between any of the three conditions was observed. However, we found increased susceptibility to serious infections as the number of conditions increased with individuals with at least two conditions had 2.6-fold increased risk of infections.
Parikh: Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Verastem Oncology, and AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics, MorphoSys, Janssen, AstraZeneca, TG Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, AbbVie, and Ascentage Pharma: Research Funding. Dispenzieri: Takeda: Research Funding; Alnylam: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Consultancy; Sorrento Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Murray: Mayo Clinic: Other: Has received patents for the Mass-Fix technology which has been licensed to the Binding Site with potential royalties.. Kumar: Astra-Zeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; KITE: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Antengene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Tenebio: Research Funding; Roche-Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Carsgen: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Adaptive: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding. Cerhan: Regeneron Genetics Center: Other: Research Collaboration; Genentech: Research Funding; Celgene/BMS: Other: Connect Lymphoma Scientific Steering Committee, Research Funding; NanoString: Research Funding. Kay: TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Morpho-sys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Targeted Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Oncotracker: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sunesis: Research Funding; MEI Pharma: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol Meyer Squib: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Rigel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Behring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CytomX Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Dava Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Shanafelt: Genentech, Pharmacyclics: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal